



PBSCT:Peripheral stem cell transplantation周邊血液幹細胞移植
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation(PBSCT), also called peripheral stem cell support, is a method of replacing blood-forming stem cells destroyed, for example, by cancer treatment.
PBSCT is now a much more common procedure than its bone marrow harvest equivalent, this is in-part due to the ease and less invasive nature of the procedure.
Studies suggest, that PBSCT has a better outcomes in terms of the number of hematopoietic stem cell(CD34+ cells)yield.[4]
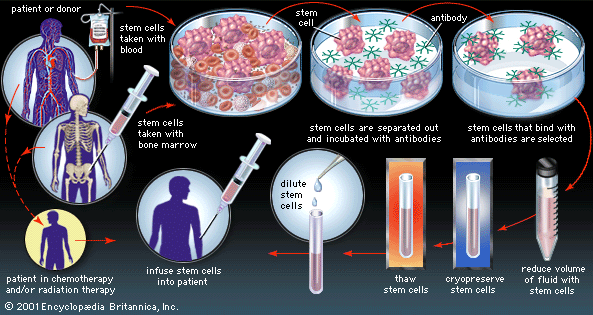
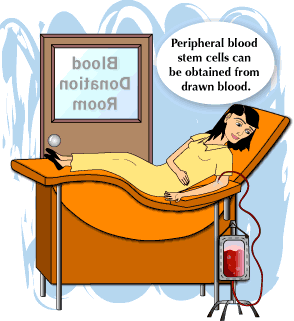
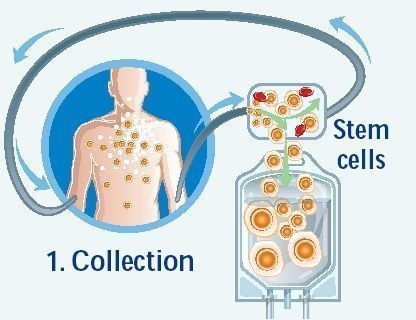
Immature blood cells hematopoietic stem cells in the circulating blood that are similar to those in the bone marrow are collected by apheresis from a potential donor(PBSC collection). The product is then administered Intravenously to the patient after treatment.
The administered hematopoietic stem cells then migrate to the recipients bone marrow, a process known as Stem cell homing, where the transplanted cells override the previous bone marrow. This allows the bone marrow to recover, proliferate and continue producing healthy blood cells.
The transplantation may be Autologous(an individual's own blood cells saved earlier), Allogeneic(blood cells donated by someone else with matching HLA), or Syngeneic(blood cells donated by an identical twin).
The procedure typically lasts for 4~6 hours, depending on the donors total blood volume.
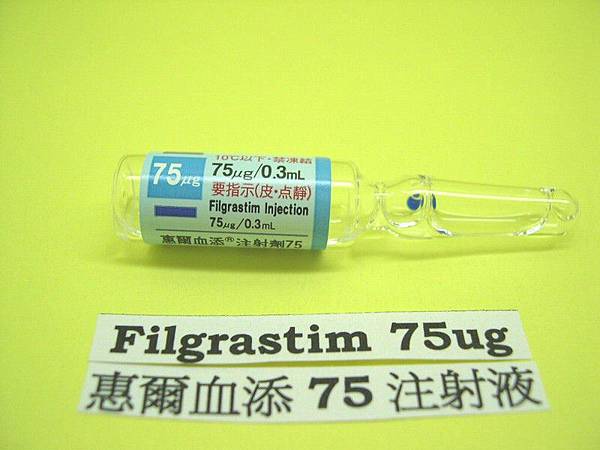
Granulocyte colony stimulating factor(GCSF)are naturally occurring glycoproteins that stimulate white blood cell proliferation. Filgrastim is a synthetic form of GCSF produced in E.coli.
PBSC donors are given a course of GCSF prior to PBSC collection, this ensures a better outcome, as stem cell proliferation increases, thus increasing the number of peripheral stem cells in circulation. The course is usually given over a 4 day period prior to PBSC collection. Mild bone pain usually results due to the excessive stem cell crowding within the bone marrow.
Since allogeneic PBSCT involves transformation of blood between different individuals, this naturally carries more complications than autologous PBSCT. For example, calculations must be made to ensure consistency in the amount of total blood volume between the donor and recipient. If the total blood volume of the donor is less than that of the recipient(such as when a child is donating to an adult), multiple PBSCT sessions may be required for adequate collection. Performing such a collection in a single setting could result in risks such as hypovolemia, which could lead to cardiac arrest, thus health care providers must exercise careful precaution when considering donor-recipient matching in allogeneic PBSCT.
何謂周邊血液幹細胞移植?
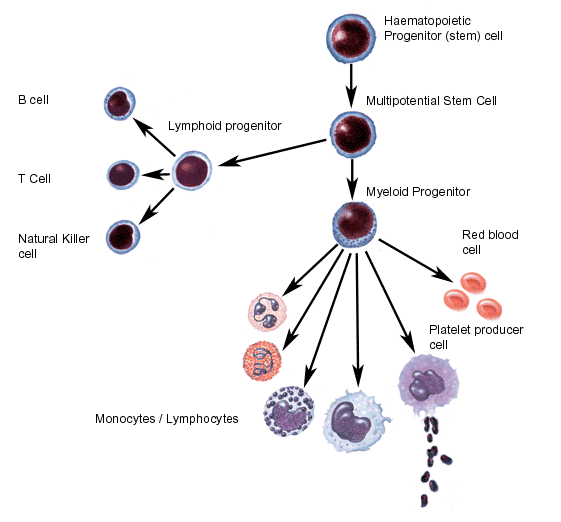
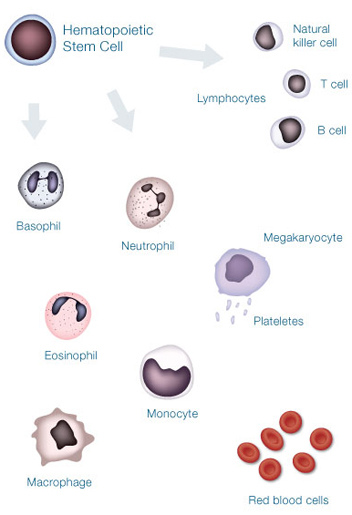
造血幹細胞(Stem cell)平常在骨髓內負責人體白血球,紅血球及血小板的製造,人類出生之後造血幹細胞主要分佈在人體的骨髓中,而周邊血液的造血幹細胞含量極低,無法分離得到足夠幹細胞作為臨床移植用。但是在病人接受高劑量的化學藥物治療,當白血球回升之際,骨髓中的幹細胞會被釋放至周邊血液中,若合併使用GCSF效果更好,才能抽取足夠的幹細胞,經過收集、分離、保存,然後回輸。
周邊血液幹細胞是在1990年代被發展出來的,主要是因為許多病患接受高劑量的化療或TBI,這些治療的毒性主要發生在骨髓造血細胞,一旦骨髓造血細胞被破壞,就無法被抽取利用;然而如事先收集起來的周邊血幹細胞則不受影響,因此可以用於重建骨髓造血細胞的功能。
周邊血液幹細胞移植的優點
-
不需住院行全身麻醉抽取幹細胞,因此可免除因抽取導致的疼痛及麻醉的危險。
-
比骨髓移植較不受污染,可降低感染、死亡及住院天數。
-
移植後紅血球、白血球的恢復速度加快,血小板的恢復也比骨髓移植快14天以上,使輸血小板次數減少,降低因輸血的致病率及死亡率。
-
降低成本,且有經濟效益。
周邊血液幹細胞移植的用途
-
固態腫瘤的病患接受高劑量治療後,在癌細胞侵犯骨髓時,採用周邊血液幹細胞可減少癌細胞污染的可能性。
-
曾經接受骨盆腔放射線治療,無法從骨髓抽取足夠造血細胞進行自體骨髓移植者,周邊血液細胞是最好替代來源。
-
異體骨髓移植的骨髓移植捐贈者,因故無法收集骨髓時,也可用周邊血液幹細胞來代替。



 留言列表
留言列表
