Pyroptosis
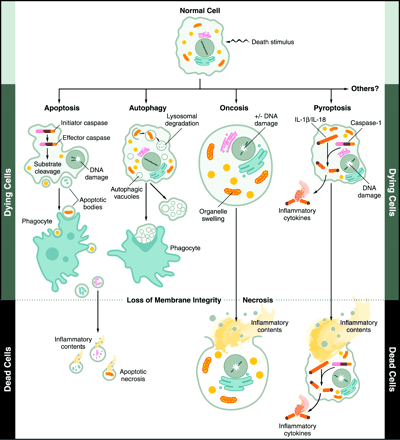
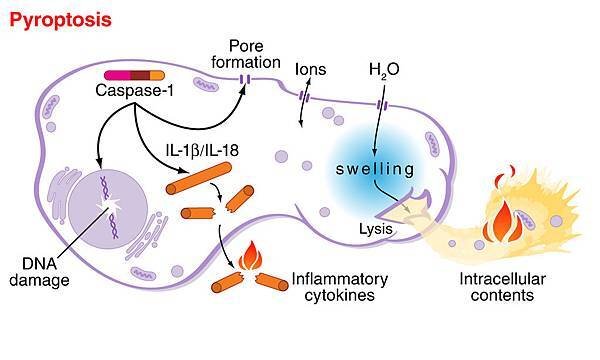
Pyroptosis is a form of Programmed cell death associated with Antimicrobial responses during Inflammation.
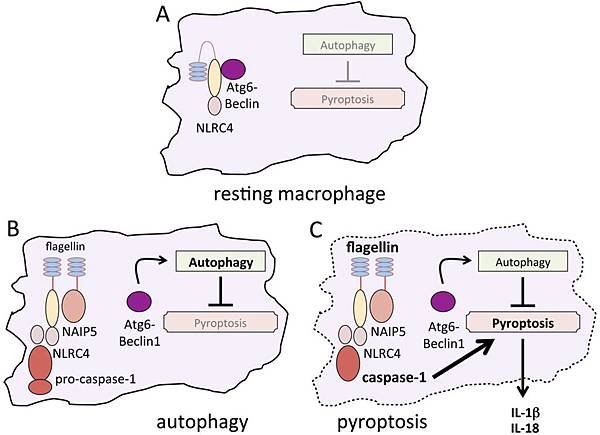
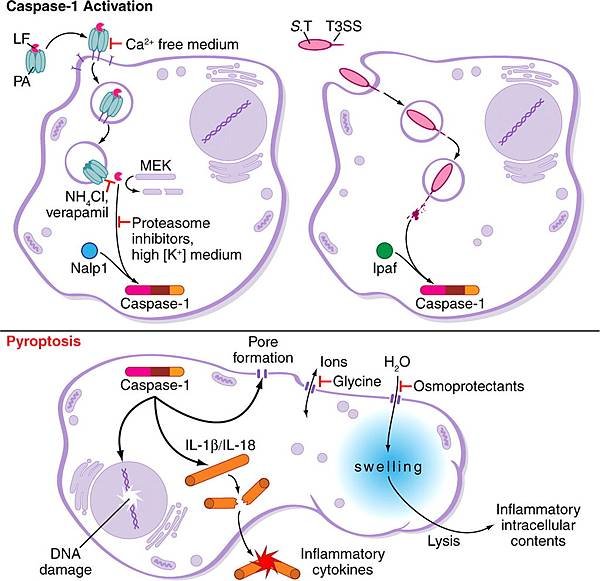
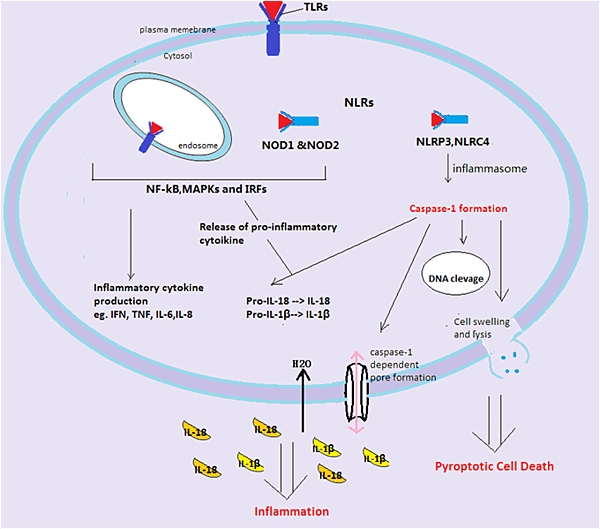
In contrast to apoptosis, pyroptosis requires the function of Caspase-1, and has been studied in the context of Salmonella-infected macrophages. The initiation of pyroptosis has been linked to the recognition of Flagellin components of Salmonella and Shigella species (and similar Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) in other microbial pathogens) by NOD-like receptors (NLRs). These receptors function like plasma membrane Toll-like receptors (TLRs), but recognise intracytoplasmic antigens rather than extracellular ones.
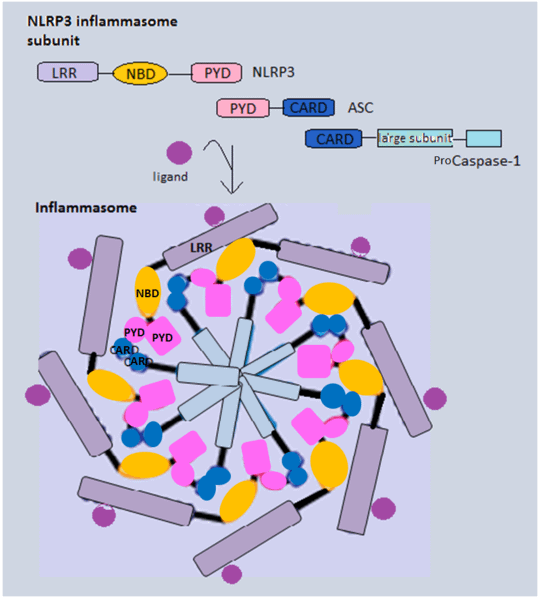
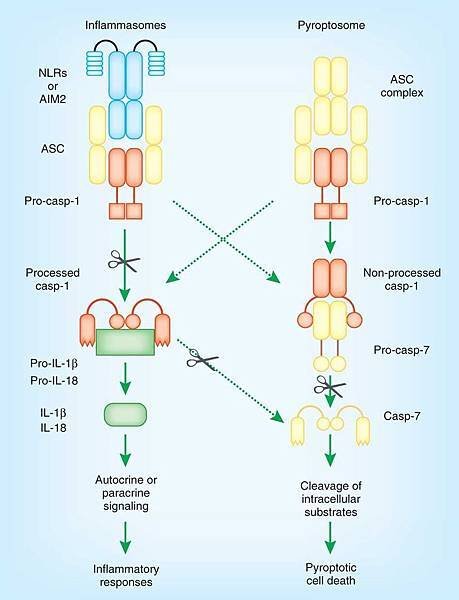
Recently, it was shown that Caspase-1 is activated during pyroptosis by a large supramolecular complex termed the Pyroptosome (also known as an Inflammasome).
Only one large Pyroptosome(Inflammasome)is formed in each macrophage, within minutes after infection. Biochemical and Mass Spectroscopic analysis revealed that this pyroptosome is largely composed of dimers of the adaptor protein ASC (apoptosis-associated speck protein containing a CARD or Caspase activation and recruitment domain).
Unlike apoptosis, Pyroptosis results in the release of Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and Cytokines that activate pro-inflammatory immune cell mediators.
Summary of the different Morphologies, Mechanisms and Outcomes of the 3 forms of cell death:Apopotosis, Pyroptosis and Necrosis
|
|
Characteristics |
Apoptosis |
Pyroptosis |
Necrosis |
|
Morphology |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cell lysis |
X |
O |
O |
|
|
Cell swelling |
X |
O |
O |
|
|
Pore formation |
X |
O |
O |
|
|
Membrane blebbing |
O |
X |
X |
|
|
DNA fragmentation |
O |
O |
O |
|
Mechanism |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Caspase-1 |
X |
O |
X |
|
|
Caspase-3 |
O |
X |
X |
|
|
Cytochome-c release |
O |
X |
X |
|
Outcome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inflammation |
X |
O |
O |
|
|
Programmed cell death |
O |
O |
X |



 留言列表
留言列表
