Treatment of De Quervain's Syndrome with ultrasound(US)-guided infiltration of steroids and hyaluronic acid
(http://posterng.netkey.at/esr/viewing/index.php?module=viewing_poster&task=&pi=122142)
Congress : ECR 2014
Poster No. : C-2052
Type : Scientific Exhibit
Keywords : Outcomes, Inflammation, Puncture, Ultrasound, Percutaneous, Musculoskeletal system, Interventional non-vascular
Authors : L. Turturici1, E. Tarabelli2, R. Giuliani2, I. G. Burrelli2, P. Vagli1, P. Bemi1, C. Vignali2; 1Pisa/IT, 2Lido di Camaiore/IT
DOI : 10.1594/ecr2014/C-2052
DOI-Link : http://dx.doi.org/10.1594/ecr2014/C-2052

Fig. 1 : The images show the location of pain and the course of the two tendons near the radial styloid process. References: U.O.C. Radiologia, Versilia Hospital, AUSL 12 of Viareggio, Lido di Camaiore/Italy 2013
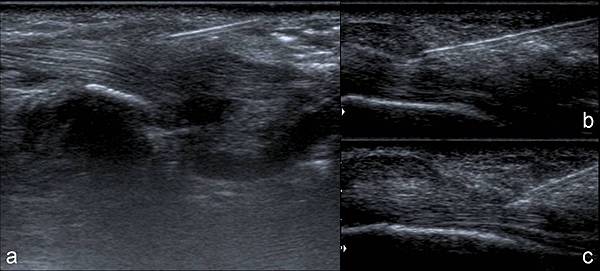
Fig. 4 : US monitoring during the procedure: immediately after the needle puncture local anhestesia is performed (a), the needle tip is inserted into the common tendon sheath (b), during steroids and hyaluronic acid injection a sheath distension (arrow heads) can be appreciated (c). References: U.O.C. Radiologia, Versilia Hospital, AUSL 12 of Viareggio, Lido di Camaiore/Italy 2013
Aims and objectives
To evaluate the effectiveness of US-guided infiltration of Hyaluronic acid (HA) and Steroids in the common tendon sheath of the Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and Abductor pollicis longus (APL) in the De Quervain's Syndrome in order to obtain a regression of the clinical status with functionality improvement and possibly avoiding a surgical intervention. De Quervain’s Syndrome is a Stenosing tenosynovitis of the First dorsal compartment of the wrist, affecting the EPB and APL tendons...
Methods and materials
34 patients with De Quervain's Syndrome were evaluated with US (fig.2) and treated with US-guided infiltration of HA and steroids. The procedure was performed percutaneously, using a sterile technique (fig.3), under US-guidance and with local anesthesia, puncturing selectively the common tendons sheath of the EPB and the APL with a 21G needle for the injection of steroids and low molecular weight (750 kDa) HA. US continous monitoring (with a 7-12 MHz linear transducer) depicted the...
Results
Three months after the procedure, a clinical improvement up to 80% reduction of QuickDASH score indexes was recorded in 28/34 patients (82.3%), while 6 patients (17.6%) had no regression of clinical symptoms and were retreated (tab.1). At 6 months follow-up 30 patients (88.2%) achieved a significant reduction of scores except for 4 patients (11.8%) that required a new treatment (tab.2). At 12 months follow-up an important clinical relief occurred in all patients, except 4 patients that...
Conclusion
Our data show that Selective infiltration under US-guidance of both Steroids and Hyaluronic acid in the common sheath of the EPB and APL provides a significative improvement of pain and function in the majority of patients affected by De Quervain’s Syndrome avoiding a possible surgery.
Personal information
Emilio Tarabelli MD, U.O.C. Radiologia, Versilia Hospital, AUSL 12 of Viareggio, Lido di Camaiore, Italy; emiliorx@libero.it
Riccardo Giuliani MD, U.O.C. Radiologia, Versilia Hospital, AUSL 12 of Viareggio, Lido di Camaiore, Italy; giuliani@sirius.pisa.it
Italo G Burrelli MD, U.O.C. Radiologia, Versilia Hospital, AUSL 12 of Viareggio, Lido di Camaiore, Italy; italoburrelli@yahoo.it
Paola Vagli MD, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology.



 留言列表
留言列表
