
Granzymes:Serine proteases,顆粒溶解酶
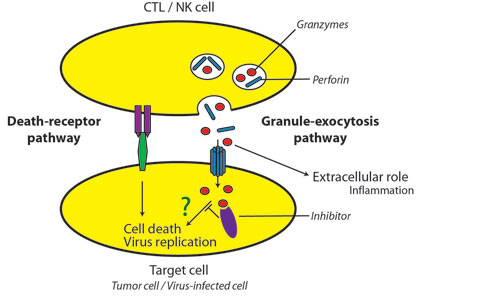
Granzymes are Serine proteases that are released by Cytoplasmic granules within Cytotoxic T cells and Natural killer cells.
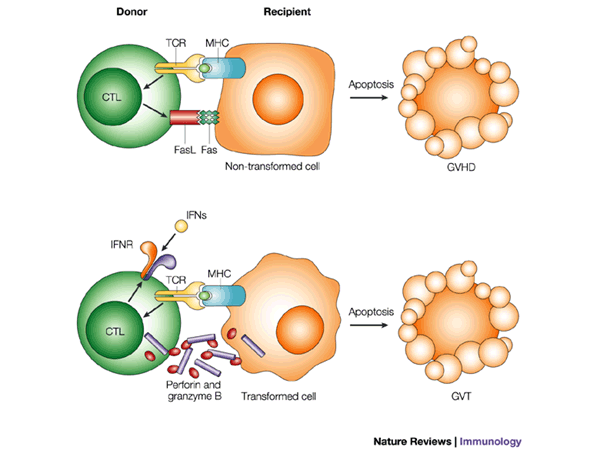
Their purpose is to induce apoptosis within virus-infected cells, thus destroying them.
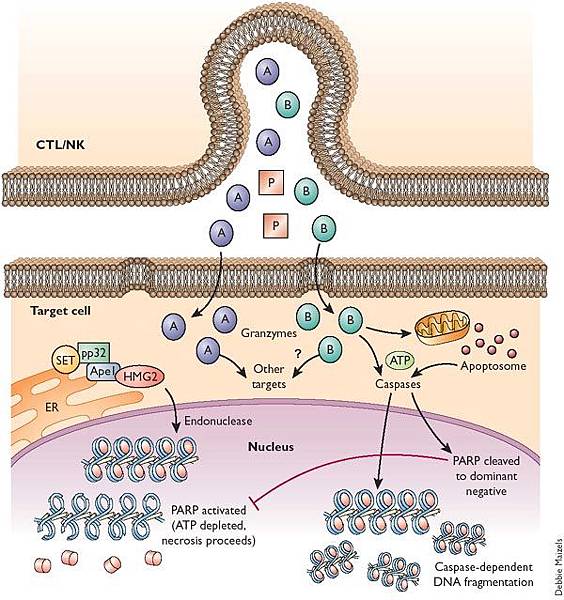
Granzymes when in the host cell are contained in cytotoxic granules to prevent harm to the host cell. Other locations that granzymes can be detected are in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, and the trans-Golgi reticulum. The goal of the granules and perforins is to create a path way for the granzymes to follow and enter the target cells cytosol.
Granzymes are identified as being part of the serine esterase family.
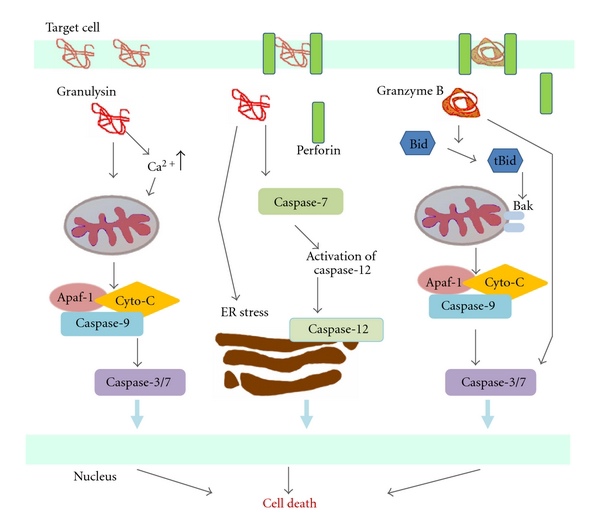
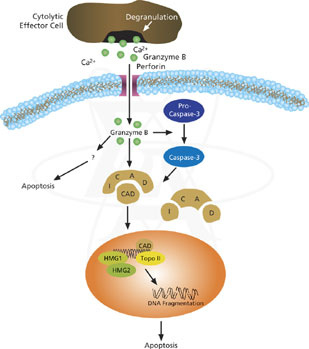
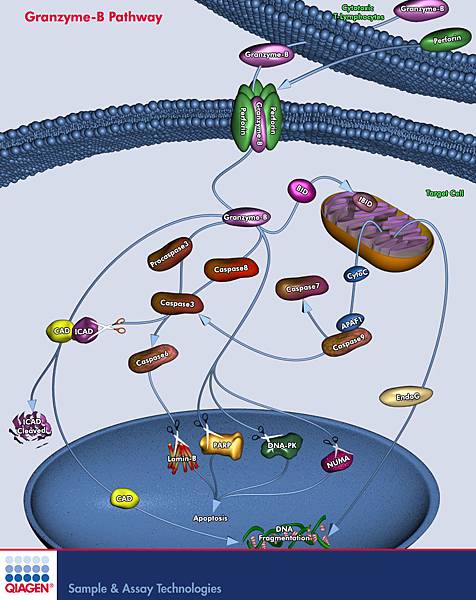
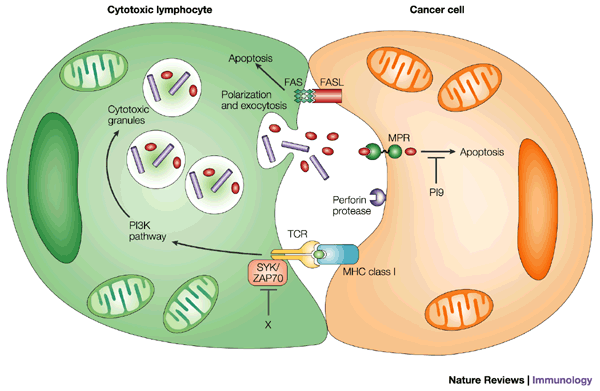
Cytotoxic T cells and Natural killer cells release a protein called Perforin, which attacks the target cells. Researchers used to think that perforin creates pores within the cell membranes, through which the granzymes can enter, inducing apoptosis. However, new evidence indicates that a multimeric complex(Granzyme B, Perforin, and granulysin)can enter a cell through the Mannose 6-phosphate receptor or another receptor found in tumor cells and is enclosed in a vesicle or a sac. Perforin then allows GrB to pass through the vesicle surface and into the cell, causing apoptosis by various pathways.
They do so by cleaving caspases, especially Caspase-3, which in turn activates Caspase-activated DNase. This enzyme degrades DNA, thus inducing apoptotic cascades. Also, GrB cleaves the protein Bid, which recruits the protein Bax and Bak to change the membrane permeability of the mitochondria, causing the release of cytochrome c(which is one of the parts needed to activate caspase-9 via the Apoptosome), Smac/Diablo and Omi/HtrA2(which suppress the Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins,IAPs), among other proteins. As well, GrB is shown to cleave many of the chemicals responsible for apoptosis without the aid of caspase, as proven by experiments on caspase knockout mice CTL cells incubated with other cells.
In 1986 Jürg Tschopp and his group published a paper on their discovery of granzymes. In the paper they discussed how they purified, characterized and discovered a variety of granzymes found within cytolytic granules that were carried by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Jürg was able to identify 8 different granzymes and discovered partial amino acid sequences for each. The molecules were unofficially named Grs for five years before Jürg and his team came up with the name granzymes which was widely accepted by the scientific community.
Granzyme secretion can be detected and measured using Western Blot or ELISA techniques. Granzyme secreting cells can be identified and quantified by flow cytometry or ELISPOT. Alternatively, granzyme activity can be assayed by virtue of their protease activity.



 留言列表
留言列表
